What makes the cryptocurrency market so tough and immune? Undoubtedly it is the strategically established Cryptocurrency exchange market that support one and every function of the financial ecosystem. Just like a trade market for financial stocks, Cryptocurrency exchanges serve as a platform and promote the virtual trade of cryptocurrencies. On the whole, cryptocurrency exchanges are the backbone of the cryptocurrency commerce.
Cryptocurrency exchanges are of two types- Centralized and Decentralized. In this article, you will learn about decentralised exchanges, what sets them apart from centralised exchanges, how it affects the cryptocurrency ecosystem, features of decentralised exchanges and some renowned decentralised cryptocurrency exchange projects.
Centralized Vs. Decentralized Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Decentralised cryptocurrency exchanges are dependent on centralised exchange rates. The two trades defined into:
Centralized Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Centralized exchanges are a neutral third-party whose primary function is to facilitate any transaction or transfer between two parties. These cryptocurrency stock exchanges match individuals search for cryptocurrency with institutions offering the same. This type of trading minimises market friction by boosting liquidity and providing convenience of trade. The transactions go through an account that holds funds and positions. Here liquidity refers to the ability of the market to allow buying and selling of a commodity at a stable price. Some famous example of centralised cryptocurrency exchanges is Coinbase, Binance, Kraken and more.
Decentralized Cryptocurrency Exchanges
Contrary to centralised exchanges, decentralised cryptocurrency exchanges have different controlling authority. The trade here is run similar to the cryptocurrency ecosystem itself- distributed ledger network. It implies that no single account holds the coins, positions or information, instead the exchange acts as a mediator whose primary function is to matching trade orders and channelize them. There is no third party server controlling the transactions neither you have to pay an escrow amount to the intermediary.
Let us discuss this in details to have a better picture of the subject.
Difference between Centralized and Decentralized Cryptocurrency Exchanges:
The two types of exchanges differ from each other on a variety of attributes. A few of them include
Control of Funds
In a centralised exchange, the deposits in the exchange facilitate the transaction, implying that the third-party server manages funds deposited in the custody of the exchanges.
On the contrary, in decentralised exchanges, there is no central server and individuals are free to connect with their peers to transact as per their will. All the participants take control of their assets and negotiate with each other.
Anonymity
Earlier, there are a few centralised exchanges that allow users to maintain their anonymity, or, they have to settle with decentralized exchanges . However, with stringent government policies and regulations, it is now mandatory to fulfill KYC and AML laws. This makes it tough to trade anonymously on a centralised platform.
When it is decentralised, it directly implies that you do not have to disclose your identity to trade on the ecosystem. These exchanges are a mirror image of distributed blockchains.
Authentication
In centralised exchanges, every transaction demands approval from exchange authority. Here, the cryptocurrency exchange works as a third party intermediary that ensure trusted crypto services.
There is no such provision in a decentralised exchange. There are some blockchain protocols like smart contracts that allow users to transact without authentication and authorisation issues.
Advantages of Decentralised Exchanges
In many ways, decentralised trades are better than centralised exchanges. These features include:
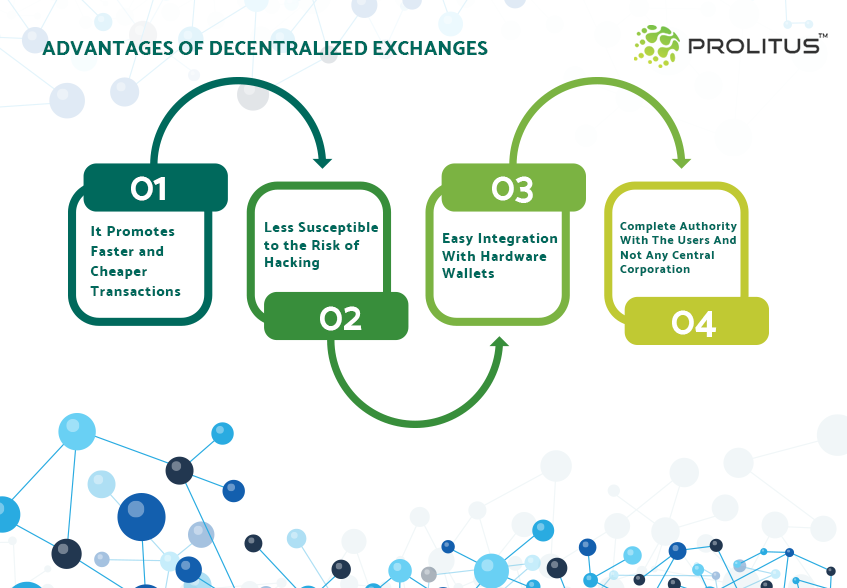
It Promotes Faster and Cheaper Transactions
As there is no third party involved in the trade, the speed of the operation under decentralised exchanges is more rapid than its counterparts. Similarly, users do not have to pay a fee or commission for authenticating and authorising a transaction which makes it cheaper and attractive for crypto-enthusiasts.
Less Susceptible to the Risk of Hacking
In comparison to centralised exchanges, decentralised models are less vulnerable to hacking threats. There are ample instances when high-profile hackers have attacked centralised platform and disclosed the risk. But with the decentralised model, there is no one entry to the ecosystem, and thus there is no authority left with the hacker. For safekeeping of the process, a hacker has to take charge of more than half of the chain which isn’t feasible.
Easy Integration With Hardware Wallets
One added advantage of decentralised exchanges is that you can easily integrate them with many reputed hardware wallets. The list includes names like Trezor and Ledger Nano S. This increases the safety level of the transactions. Thereby allowing users to send money from their e-wallets to smart contracts present on the decentralised exchanges.
In case of centralised exchanges, a user has to enter a manual pin to move the money which makes the system prone to malicious phishing and keylogging attacks.
Complete Authority With The Users And Not Any Central Corporation
Based on the P2P network, the money invested in a decentralised exchange remains under the custody of the user only. The transactions are facilitated using smart contracts which in turn are run by private keys of the users.
Demerits of Decentralized Exchanges
Every good thing comes with some flaws, and so do decentralised exchanges. The model suffered from some practical problems initially, but over the period, things have changed dramatically about safety and reliability. Some of the loopholes in the system included:
Usage Complicacies
What made some centralised exchanges so popular among the traders? It was the ease of use they offered to the people willing to participate in the market. You only have to take care of your email and password and need not worry about any private keys. Decentralized exchanges lack this simplicity which makes them weaker regarding user-friendliness and hassle-free experiences.
Limited Functionality
When compared with their centralised counterparts, decentralised exchanges offer restrained functionality. There is no limit of order available which restricts the order type, and because of low trade volume, the user does not enjoy the breadth of coins to trade. Also, decentralised exchanges are made to support only basic cryptocurrencies. Some other features that are missing with decentralized exchanges is margin trading, stop loss and more. This makes it a less popular ecosystem in the immense cryptocurrency commerce environment.
Low Volume Of Trade
With limited functionality given, decentralised exchanges fail to impress audience resulting in low footfalls and abysmally questionable transaction volume. Simply putting into perspective, if you are willing to invest in a decentralised exchange, it is tough and time taking to find a counterparty to trade with.
Also Read: How Cryptocurrencies Work – A Technical Perspective
Details Of Existing Decentralised Exchange Projects
There are a handful of decentralised exchange projects running currently. Let us talk about a few popular ones:
Ox Protocol
The white papers of Ox Protocol describe them as “we describe a protocol that facilitates low friction peer-to-peer exchange of ERC20 tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. The protocol is intended to serve as an open standard and common building block, driving interoperability among decentralised applications (dApps) that incorporate exchange functionality. Trades are executed by the system of Ethereum smart contracts that are publicly accessible, free to use and that any dApp empower quick trading. DApps built on top of the protocol can access public liquidity pools or create their liquidity pool and charge transaction fees on the resulting volume.”
The entire system based on broadcast protocols called “relayers.”, Make transaction simpler and high yielding. These layers are responsible for broadcasting the orders to the network. This broadcast accepted by a party streamlines transactions. For each successfully closed trade, the relayer is incentivised in ZRX token which is a domestic token of the protocol. Radar Relay is an excellent example of relayer.
Kyber Network
Referred as an instant network, Kyber network executes instant on-chain exchanges of cryptocurrencies. The final objective and a variety of features of Kyber networks are similar to the Ox Protocol. However, the former promotes on-chain transactions. The protocol also works on the problem of low trade volume in the ecosystem which is one of the primary shortcomings that makes decentralised exchanges less famous.
Also, here the cost of maintaining order book is lower than other protocols.
The protocol uses Dynamic Reserve Pool to maintain liquidity. To keep the exchange rates competitive and ensuring that no centralisation occurs, this network provides a few entities readily available in the system. There are some safety measures put to use for preventing concentration from happening. The domestic token of the network is named as Kyber Network Crystal (KNC) which is an ERC20 token.
Etherdelta
It is the most popular decentralised exchange, and the majority of ERC20 coins that have offered their Initial Coin Offering (ICO) would first be listed on Etherdelta and then on other exchanges. It allows users to invest in the coins much before they get enlisted on the popular centralised platform like Bittrex or Binance and get expensive.
OmiseGO
The whitepaper of the company explains “OmiseGO is building a decentralised exchange, liquidity provider mechanism, clearing house messaging network, and asset-backed blockchain gateway. Any single one party does not own OmiseGO. Instead, it is an open distributed network of validators which enforce behaviour of all participants. It uses the mechanism of a protocol token to create a proof-of-stake blockchain to enable enforcement of market activity amongst participants.
This high-performant distributed network enforces exchange across asset classes, from fiat-backed issuers to fully decentralised blockchain tokens (ERC-20 style and native cryptocurrencies). Unlike nearly all other decentralised exchange platforms, this allows for the decentralised exchange of other blockchains and between multiple blockchains directly without a trusted gateway token.” It is one of the most ambitious decentralised exchanges and is working on building a network where users can trade in any currency.
Airswap
The Airswap white papers define it as “we present a peer-to-peer methodology for trading ERC20 tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. First, we outline the limitations of blockchain order books and offer a strong alternative in peer-to-peer token trading: off-chain negotiation and on-chain settlement. We then describe a protocol through which parties can signal to others their intent to trade tokens. Once connected, counterparties freely communicate prices and transmit orders among themselves. During this process, parties may request prices from an independent third party oracle to verify accuracy. Finally, we present an Ethereum smart contract to fill orders on the Ethereum blockchain.” This exchange is pretty similar to Ox except that Airswap functions with off-chain negotiations while Ox is based on relayers.
Conclusion:
Indeed! Decentralised exchanges display the great potential to be the next big thing with a lot of benefits for the users. It is now the most exciting phase to wait for this technology to bloom to its full potential and impact the existing cryptocurrency market.